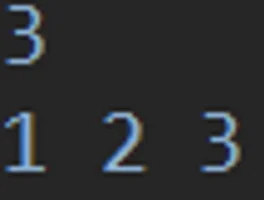728x90
반응형
코테에서 기본의 기본이 되는 완전탐색 기법!
아래의 코드를 충분히 익혀 완탐 문제는 틀리지 않도록 연습하자.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
static int M;
static int pCnt = 0, cCnt = 0, ppCnt = 0, ccCnt = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
M = sc.nextInt();
//1. 순열
perm(0, new int[M], new boolean[arr.length]);
System.out.println("순열: "+ pCnt);
//2. 중복순열
// 위와 비슷하게 예시 작성
}
// 1. 순열 (nPm)
// cnt: 뽑으려는 개수, selected: 선택된 수, visited: 배열 방문관리
static void perm(int cnt, int[] selected, boolean[] visited) {
if(cnt==M) { // 기저조건
pCnt++;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
System.out.print(selected[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true; // 방문 처리
selected[cnt] = arr[i]; //배열의 i 번째 선택하기
perm(cnt+1, selected, visited); // 다음 순열 뽑기
visited[i] = false; // 방문 처리 풀음
}
}
}
// 2. 중복 순열 (nㅠm)
// 중복 가능하므로 방문관리 할 필요 없음
static void pperm(int cnt, int[] selected) {
if(cnt == M) {
ppCnt++;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
System.out.print(selected[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
selected[cnt]=arr[i];
pperm(cnt+1, selected);
}
}
// 3. 조합 (nCm)
// cnt: 조합 개수, selected: 뽑힌 수, startIdx: 배열에서 순서 관리
static void comb(int cnt, int[] selected, int startIdx) {
if(cnt == M) {
cCnt++;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
System.out.print(selected[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i=startIdx;i<arr.length;i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
comb(cnt+1, selected, i+1);
}
}
//4. 중복 조합 (nHm)
static void ccomb(int cnt, int[] selected, int startIdx) {
if(cnt == M) {
ccCnt++;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
System.out.print(selected[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i=startIdx;i<arr.length;i++) {
selected[cnt] = arr[i];
ccomb(cnt+1, selected, i);
}
}
}728x90
반응형
'알고리즘 > 개념' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [개념] 완전 탐색 기법 - 부분집합 편 (Java) (0) | 2021.07.14 |
|---|---|
| [개념] 메모이제이션 기법에 대하여 (0) | 2021.01.19 |